Best Diabetic and Neuropathy Hospital in Lokapur
Diabetic Foot and Neuropathy
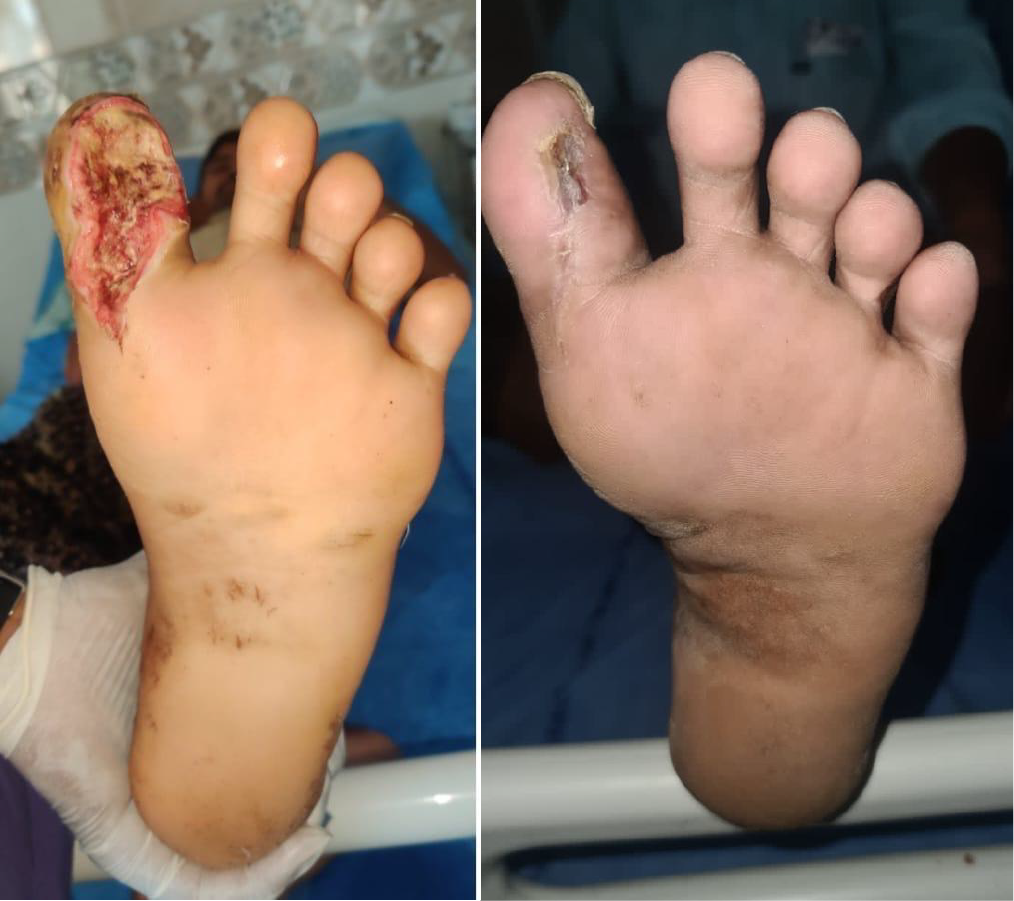
Diabetic Foot refers to complications resulting from poorly managed diabetes, often characterized by foot ulcers, infections, and deformities. Diabetic Neuropathy is a frequent underlying condition, leading to nerve damage that reduces sensation in the feet and increases vulnerability to injuries.
Key Characteristics:
- Loss of protective sensation due to peripheral neuropathy.
- Poor circulation (peripheral arterial disease), delaying wound healing.
- Deformities such as claw toes or Charcot foot.
- Increased susceptibility to infections due to impaired immunity.
Risk Factors:
- Long-standing diabetes with poor glycemic control.
- Smoking, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
- Previous history of foot ulcers or amputations.
- Inappropriate footwear causing pressure points.
Complications:
- Chronic non-healing ulcers.
- Wet gangrene (infected tissue with pus and foul smell).
- Dry gangrene (tissue death without infection, presenting with darkened, shriveled areas).
- Osteomyelitis (bone infection).
- Amputation in severe cases.
Treatment Options
Non-Surgical Approaches:
Regular Dressing and Wound Care:
- Use of antiseptics and advanced dressings (e.g., hydrocolloid, foam, or silver-impregnated).
- Frequent debridement of necrotic tissue.
Diabetic Foot Care:
- Proper footwear to reduce pressure and prevent injuries.
- Regular foot inspections and hygiene maintenance.
Management of Neuropathy:
- Medications like pregabalin, gabapentin, or duloxetine for neuropathic pain.
- Vitamin B12 and alpha-lipoic acid supplements for nerve health.
Ozone Therapy:
- Promotes tissue oxygenation and microbial control.
- Can improve wound healing in resistant ulcers.
Treatments for Gangrene:
Wet Gangrene:
- Aggressive debridement or minor amputation if necessary.
- Antibiotics targeting polymicrobial infections.
- Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) in selected cases.
Dry Gangrene:
- Conservative approach if not infected, allowing auto-amputation.
- Revascularization procedures to improve blood flow.
Surgical Approaches:
Revascularization:
- Angioplasty or bypass surgery to restore circulation.
Major Surgery:
- Partial or total amputation for severe, non-salvageable infections.
- Limb salvage surgeries to preserve function.
Preventive strategies, including tight glucose control, smoking cessation, and early detection, remain critical in reducing the incidence and severity of diabetic foot complications.